Forced Oscillations and Resonance
In this article, we are going to study about Forced Oscillations and Resonance.
 Table of Contents
Table of Contents- Forced Oscillations
- Resonance
Forced Oscillations
There are two kinds of Oscillations:
- Free Oscillations: When a system, such as a pendulum or a spring, is displaced from its equilibrium position and released, it starts oscillating. If no external force is maintaining this oscillation, the system will oscillate with its natural frequency. Such oscillations are called free oscillations. Free oscillations die out with time due to the presence of damping forces, such as friction, air drag, etc.
 Note
NoteA big and complex structure (e.g. a building, bridge, etc.) may have multiple natural frequencies.
- Forced or Driven Oscillations: If an external force is maintaining the oscillations, we call them Forced or Driven Oscillations. For example, when a child on a swing keeps getting pushed by his mother, so as to maintain his oscillations. In such cases, the oscillator initially oscillates with its natural frequency. But after an external periodic force is applied, the oscillator slowly starts oscillating with the (angular) frequency of the external periodic force.
Now, what about the amplitude of oscillations?
Amplitude of oscillation is a function of the natural frequency and forced frequency.
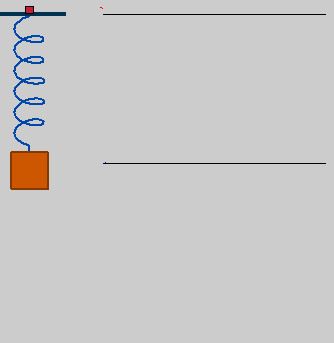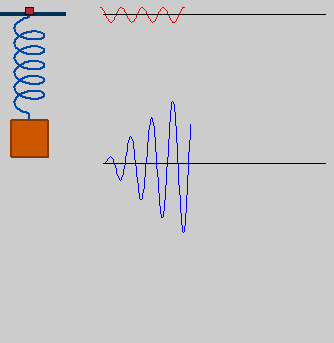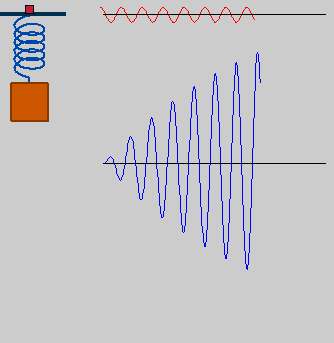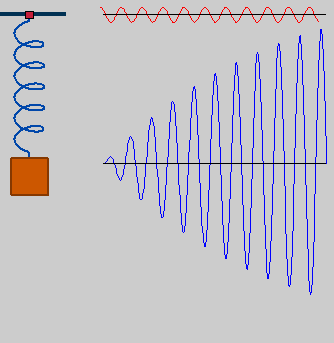
But what if the forced frequency is almost equal to the natural frequency? – Here, the concept of Resonance comes into the picture.
 Note
NoteThe maximum possible amplitude depends on the driving frequency, as well as on the damping forces. That’s why its value is never infinity.
Resonance
When the forced frequency of the driving force being applied on an oscillating object (i.e. oscillator) is close to the natural frequency of that oscillator, the amplitude of the oscillations increase substantially. This phenomenon is termed as Resonance.
Practical Applications of the concept of Resonance
The concept of Resonance finds applications in various fields, e.g. civil engineering, disaster management, etc.
- Civil engineers make sure that the natural frequency of the structure they are building is not close to the frequencies of the natural or man-made phenomenon nearby. If the natural frequency of a mechanical structure (e.g. building, bridge, aircraft, etc.) is close to the forced frequency of an external periodic force or disturbance, it might cause resonance. This will lead to the structure oscillating wildly with huge amplitude, which may eventually damage or disintegrate the structure. That’s why soldiers are ordered to go out of step while crossing a bridge. The building having its natural frequency close to that of a seismic wave will probably get much severely damaged as compared to other buildings nearby.
- If a singer can match the frequency of his sound with that of the natural frequencies of the glass utensils nearby, he/she may even break them without even touching them.